Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision in Education

Ruchir Kakkad
CEO & Co-founder
Artificial Intelligence in Education (AI) and computer vision are no longer futuristic buzzwords; they have become practical tools reshaping how students learn and how schools operate
In 2025, AI is revolutionizing classrooms by offering great opportunities for personalized learning and efficient administration. Meanwhile, computer vision is bringing new capabilities like automated attendance tracking, behavior analysis, and real-time feedback to school settings.
Education leaders, tech developers, and school administrators are witnessing a digital transformation: from adaptive learning software that tailors itself to each learner, to smart cameras in classrooms that gauge engagement.
This blog explores how AI and computer vision are transforming educational systems, covering technologies such as AI-driven learning tools, smart classroom environments, automated assessment, personalized learning, and AI in remote education.
AI is empowering a new generation of learning tools that make education more interactive and tailored. Intelligent tutoring systems and educational software can now adapt in real-time to each students needs.
For example, adaptive math platforms like DreamBox analyze a students responses and adjust the difficulty of questions on the fly, allowing learners to master concepts at their own pace. Language learning apps such as Duolingo use algorithms to personalize practice exercises based on a learners past performance. Likewise, writing assistants like Grammarly offer instant feedback on grammar and style, helping students improve their writing through real-time suggestions. These AI-driven learning tools essentially give each student a personal tutor that continuously calibrates to their level and learning style.
AI-powered tools are also making learning more engaging. Educational games and platforms use AI to dynamically adjust content and challenges, keeping students in an optimal zone of engagement.
For instance, systems like Classcraft track student behavior and reward positive actions, helping maintain a motivated classroom environment. The result is more engaged learners, interactive, adaptive experiences have been shown to boost student motivation and participation. Teachers, in turn, gain better insights: an AI system can highlight which students might be struggling or disengaged, so educators can intervene early.
In short, AI is turning learning into a two-way dialogue, where software not only delivers educational content but also listens and responds to student inputs in real time.

The modern classroom is getting smarter thanks to an array of IoT devices and AI integrations. These Smart Classroom Technology solutions create connected, responsive learning environments.
For example, IoT sensors can adjust classroom lighting and temperature automatically based on occupancy or time of day, providing a comfortable setting for students. Interactive smart boards and projectors, paired with educational software, enable multimedia lessons and instant polls or quizzes to gauge understanding. Some schools are even experimenting with IoT-based classroom management, like smart locks or voice-controlled assistants to aid teachers with routine tasks.
A core component of smart classrooms is automated attendance and monitoring. Instead of tedious roll calls, schools can use computer vision cameras to recognize students faces as they enter, instantly logging attendance with high accuracy. This saves teaching time and produces reliable attendance data without human error. Along with attendance, smart security cameras help keep campuses safe by ensuring only authorized individuals are present.
All these connected tools, from environmental sensors to facial recognition systems, feed data into dashboards that administrators and teachers can use to make informed decisions.
In essence, the classroom itself becomes an intelligent space that responds to the needs of students and staff, making the educational experience more efficient and seamless.
One of the most powerful impacts of AI in education is the ability to personalize learning like never before. Traditional one-size-fits-all teaching often leaves some students bored and others lost, but AI changes that by customizing instruction for each learner.
Personalized Learning with AI is exemplified by Adaptive Learning Platforms that dynamically adjust content. These systems assess a students skill level in real time and then tailor lessons to meet that students individual needs. If a student is struggling with a concept, the AI can provide extra practice or alternative explanations; if a student masters something quickly, the AI will introduce more advanced material to keep them challenged.
The results of this approach are impressive. Adaptive learning technology has been found to improve student mastery and retention, one study noted that adaptive platforms can boost retention rates by around 20% compared to traditional methods. Students often feel more motivated when the learning experience is tailored to them, because they arent held back or left behind. Meanwhile, teachers receive detailed analytics from these platforms, giving them a clear picture of each students progress. They can see, for example, which topics a particular student struggles with or excels in, enabling more targeted support during class or one-on-one time. In short, AI-powered personalization means every student can get a curriculum and support structure optimized for their pace and style of learning, something that was impractical at scale until now.
AI is streamlining the way students are evaluated, making assessment faster and more objective. Automated Student Assessment tools can grade exams, homework, and even complex assignments with minimal human intervention.
Multiple-choice tests have long been auto-graded, but now AI can also assess short answers and essays. For instance, platforms like Gradescope use AI assistance to grade handwritten or typed responses consistently and quickly. Advanced natural language processing algorithms enable automated essay scoring by evaluating the content and clarity of student writing. Tasks that might take a teacher many hours to grade can be completed by an AI in minutes, with detailed feedback provided to the student.
These tools not only save teachers time, they also ensure consistency and provide quick feedback. An AI grader applies the same rubric to every student, eliminating potential human bias or fatigue in scoring. And because the grading is instant, students receive feedback immediately. This kind of Real-Time Feedback in Education helps students learn from mistakes while the material is still fresh. For example, after an AI-graded quiz, a student might discover right away that all their errors were on a particular topic, allowing them to focus their review on that area.
Its important to note, however, that human oversight remains valuable, educators typically review AI-generated grades, especially for critical assessments, to ensure accuracy and fairness. Some AI scoring systems have shown quirks or errors, so teachers act as a quality check. When thoughtfully implemented, automated assessment tools can significantly reduce educators workload while maintaining, or even improving, the quality of feedback students receive.
With the growth of digital learning and remote testing, maintaining academic integrity has become a pressing challenge. AI-Based Proctoring Systems use computer vision and machine learning to monitor exams and prevent cheating, especially in remote settings.
These systems turn a students webcam and microphone into automated proctors that observe the exam environment. They can verify a students identity through facial recognition before the test begins, ensuring the right person is taking the exam. During the test, AI algorithms watch for suspicious behaviors: if a student frequently looks away from the screen, if an unknown person appears in view, or if the audio picks up other voices in the room, the system will flag those incidents.
A hallmark of AI proctoring is real-time alerts and detailed logging. If a student tries to open a website or application that isnt allowed, the AI can immediately take a screenshot and notify an instructor or human proctor. For example, one platform will alert the instructor with evidence if a test-taker attempts to open a new browser tab or access course materials during an exam. All such events are recorded: the system generates a report after the exam with timestamps of incidents and even short video clips of each flagged event. This allows instructors to review what happened and make informed judgments.
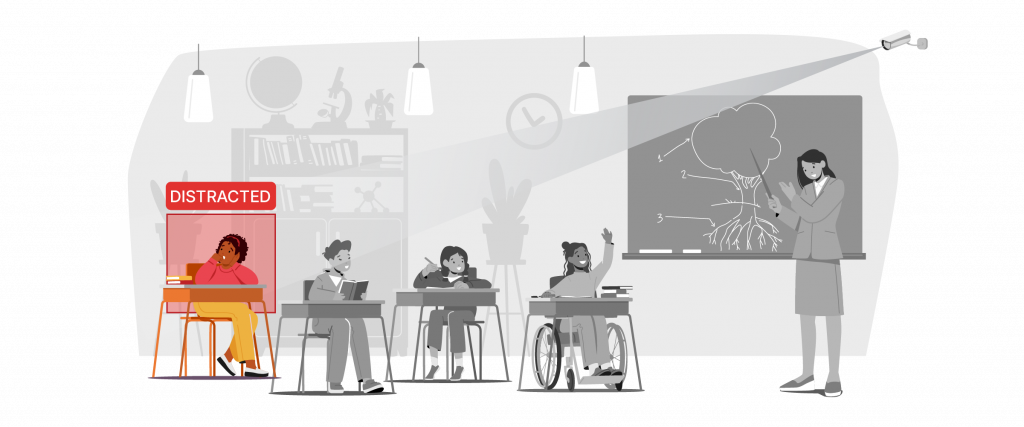

Perhaps the most transformative use of AI in physical classrooms comes from computer vision, the ability of AI systems to interpret live video feeds from cameras. Computer Vision in Classrooms means that cameras and AI algorithms work together to observe and analyze classroom activities in real time.
This ranges from simple tasks like counting how many students are present, to more nuanced ones like gauging students body language and attention. For example, a computer vision system can monitor which students are raising their hands or answering questions, providing objective data on participation. It can also detect if students are slouching, fidgeting, or consistently looking away, which might indicate disengagement. By analyzing visual cues such as facial expressions, eye gaze, and posture, computer vision notices patterns a teacher might miss.
In China, one high school that adopted AI-driven cameras to analyze student attentiveness reported that classroom behavior improved after students knew they were being monitored. While such intensive monitoring raises privacy questions, it demonstrated how data on attention can prompt positive changes in engagement.
Beyond tracking attendance or behavior, Computer Vision for Student Engagement provides actionable insights into student engagement in real time. In one study, researchers used AI to analyze live video of online classes, tracking facial cues and voice tone to measure student engagement. When a student appeared puzzled or disengaged, the system immediately alerted the teacher, prompting them to adjust their teaching strategy on the spot. If the teacher was doing most of the talking, the AI suggested involving the student more to re-capture their interest. This created a feedback loop where instruction could be dynamically tuned to student needs as the lesson unfolded. According to one report, implementing this kind of real-time AI feedback helped boost class participation significantly, in some cases, overall engagement rose by up to 40% after introducing smart monitoring tools.
Computer vision can also assist students directly through its ability to recognize images and objects. This opens up new interactive learning possibilities. For instance, Visual Recognition in Education is used in augmented reality apps that let students use a smartphone or tablet camera to explore the world. A biology student might point their device at a plant and have the app identify the species and show relevant facts. A math student stuck on a problem could snap a photo of the equation, an app like Photomath will use computer vision to read the equation and then provide step-by-step solutions.
The rise of remote and hybrid learning has made AI an indispensable ally in keeping students engaged and supported outside the traditional classroom.
AI in Remote Learning helps bridge some of the gaps of learning from home by providing support similar to in-person experiences. For example, video conferencing platforms used for classes now incorporate AI features to enhance communication. Platforms like Zoom employ AI to suppress background noise and provide live captioning of a teachers speech in real time, making lessons more accessible and clear. In fact, AI helps recreate some of the social presence of a classroom: some systems can highlight if a participant starts speaking or even detect prolonged silence or inactivity, discreetly alerting the teacher much like noticing a disengaged student in class.
AI is also boosting student support in remote environments through virtual assistants and analytics. Many online courses deploy AI chatbots as round-the-clock aides: if a student has a question after hours, the chatbot can answer common queries or provide hints, alleviating frustration until a teacher is available. These bots are often trained on course FAQs and content, allowing them to handle a surprising range of issues instantly. Additionally, AI-driven analytics track student engagement in virtual learning platforms, such as logging participation in discussion forums, completion of video lessons, or quiz attempts.
This data lets instructors spot early warning signs: for instance, if a student hasnt logged into the course for several days or is consistently missing assignments, the system can alert the instructor to reach out, much like a teacher checking in on an absent student.
While the potential of AI and computer vision in education is exciting, it also brings important challenges and ethical considerations. Privacy is a major concern whenever we introduce cameras or data-driven tools in schools. Monitoring students via video or tracking their performance generates sensitive data, so schools must ensure strict data protection. Any AI system that collects student information should comply with student privacy laws and regulations, and students and parents should be informed about what data is being collected and why. For example, if a classroom camera system analyzes student faces for engagement, the school needs clear policies on how long recordings are kept, who can access them, and how the insights are used. Transparency and consent are key to maintaining trust when using these technologies.
Another challenge is bias and fairness in AI algorithms. AI models can inadvertently reflect or even amplify biases present in their training data. In an educational context, this could mean a facial recognition system that works well for some students but not others, for instance, if it has difficulty recognizing the faces or expressions of students of certain ethnicities due to a lack of diverse data. This has been observed in some AI systems and is an active area of concern. Similarly, an automated grading system might struggle with non-standard writing styles or dialects.
Its crucial for schools and developers to test AI tools for fairness across different student groups and to use diverse training data. Keeping a human in the loop can also mitigate risks: teachers and administrators should review AI outputs (be it grades, flags, or recommendations) and apply their professional judgment, especially if something seems off or unfair.
AI and computer vision are poised to redefine the future of education. From smarter classrooms that respond to student needs in real time, to personalized learning paths for every student, these technologies offer powerful tools to enhance learning outcomes and streamline school operations.
As an education leader or innovator, the next step is to explore how these advancements can work for your institution. This is where WebOccult can help.
WebOccult is at the forefront of developing and deploying AI and computer vision solutions tailored for the education sector. We have experience turning traditional schools into smart learning spaces, for example, implementing automated attendance systems, real-time engagement analytics, and AI-driven learning platforms.
And we do so with an emphasis on privacy, customization, and seamless integration with your existing systems. The Future of Weboccult is connected with the future of education: we are committed to empowering educators and students with technology that makes learning more effective and insightful.
If youre ready to bring your institution into this future, we invite you to reach out to WebOccult. Lets talk!