Transforming Port Operations with Gate Automation Technologies

Ruchir Kakkad
CEO & Co-founder
Modern ports are very busy hubs handling thousands of truck and cargo entries and exits daily. Managing this flow efficiently is critical, especially as Indias ports and global trade volumes continue to grow.
Yet traditionally, port gate operations including verifying vehicle credentials, recording container details, inspecting cargo have been labor-intensive and prone to delays. The queues of trucks waiting at a terminal gate not only waste time but also causing extra costs, contribute to congestion, and create safety and security risks.
In an era of digital ports and smart logistics, gate automation has emerged as a game-changer.
Gate automation refers to the use of advanced technologies (like Optical Character Recognition (OCR), RFID, computer vision, AI, and IoT sensors) to automate identification and inspection processes at port entry and exit points. By reducing manual checks, automating data capture, and integrating with terminal systems, automated gates can drastically cut down turnaround times and errors. In fact, studies show ports can lose up to 15% of productivity due to manual tracking errors, a gap automation can close. Early adopters have seen impressive results, throughput boosts of 30% after deploying OCR at terminals and gate processing times halved.
This blog will explore why gate automation is critical for port authorities and logistics firms, especially in Indias fast-modernizing port sector, and delve into the core technology modules enabling it.
Efficient gate operations are the anchor of overall terminal performance. A single bottleneck at the gate can ripple through the ports entire logistics chain, causing berth delays, disturbing yard operations, and frustrating truckers and shippers.
Here are key reasons why automating gate processes has become critical:
Automated gate systems dramatically speed up truck processing, allowing many more vehicles to be cleared per hour than manual methods. By minimizing congestion and idle time, they enable quicker turnaround for each truck.
In India, DP Worlds NSIGT terminal (JNPT) introduced OCR-based smart gates that reduced the average truck gate processing from ~5 minutes down to under 1 minute. Faster gates mean higher terminal throughput and capacity without physical expansion.
Replacing manual checks with technology lowers labor requirements and errors. Fewer clerks are needed at the gate, and those remaining can focus on exceptions rather than routine data entry. Automation also reduces costly mistakes OCR and RFID ensure the right container numbers and truck details are captured accurately, avoiding downstream correction costs.
A busy port gate can be hazardous, manual operators walking among trucks or climbing to check container codes risk accidents.
Automation removes personnel from traffic lanes, thus enhancing worker safety. With ANPR (Automatic Number Plate Recognition) controlling entry, only authorized trucks get in, reducing chances of theft or unauthorized cargo removal. Every vehicle entry/exit is logged in real-time, creating a traceable audit trail for security.
Automated systems enforce standard operating procedures uniformly. They dont get tired or overlook steps during peak rush. This leads to consistent compliance with regulations, e.g. ensuring hazardous material placards are present and captured, seals are checked, and only valid container IDs pass through. Systems can automatically validate container numbers against the ISO 6346 check-digit to catch any mis-typed codes, something human eyes may miss.
To achieve the above benefits, a gate automation solution is composed of multiple integrated modules, each handling a specific aspect of the check-in/check-out workflow.
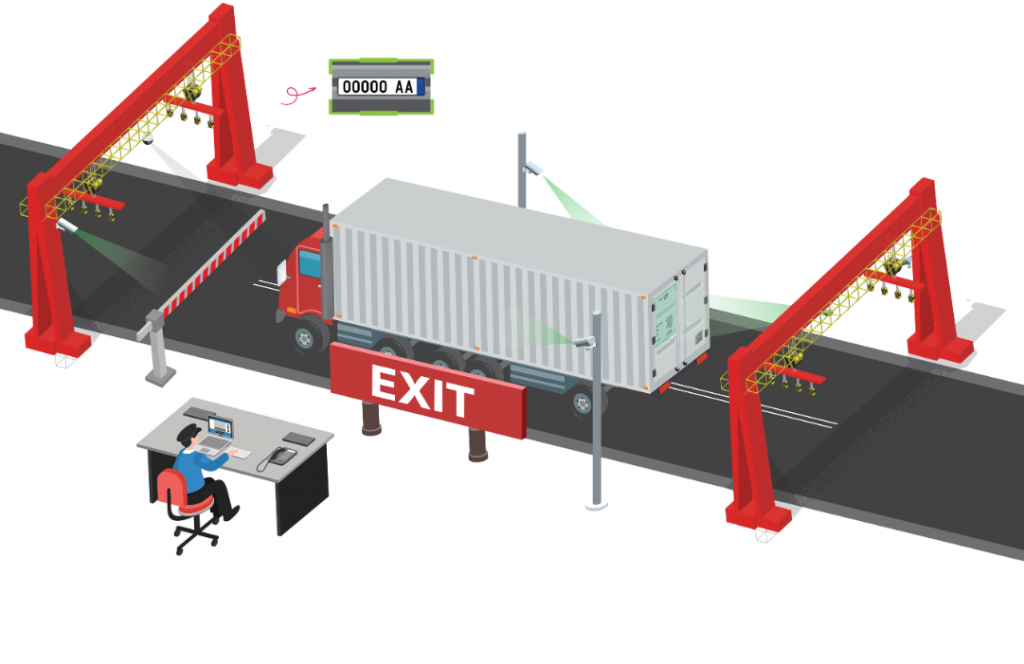
One fundamental piece is Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR), which uses cameras and computer vision to read vehicle license plates automatically. At port gates, ANPR cameras capture the trucks front or rear license plate as it approaches. OCR algorithms then extract the alphanumeric text of the plate within fractions of a second. This allows instant identification of the truck without human input.
In practice, ANPR automates the truck check-in process that was once manual. Many terminals set up a system where truck drivers pre-register their trip details (license number, container to pick up/drop off, etc.) through a port community system or appointment app.
When the truck arrives at the gate, the ANPR camera reads its plate and the system automatically pulls up the trucks appointment and assigned container info. The driver can be directed to the correct lane or yard slot immediately, often via a digital display or message, without stopping for a guard to check paperwork.
This speeds up entry and reduces gate congestion largely.
Another core module is the Container Number OCR system, which automatically reads the unique identification codes on each shipping container. Every standard container has an alphanumeric ID following the ISO 6346 format (e.g.,ABCD123456-7 with a check digit). Capturing this code correctly is vital for tracking containers through the terminal and beyond.
Traditionally, a clerk would manually note the container number or use a handheld device, a slow process prone to errors if the code is obscured or the clerk is rushed. An automated OCR setup instead uses cameras, often a multi-angle camera portal that trucks drive through, to take images of the container from the side, rear, and sometimes top.Computer vision then identifies and reads the container ID from these images.
This ensures extremely high accuracy in container identification, far beyond what manual checks achieve. One commercial system, for instance, emphasizes recognition per the ISO 6346 standard regardless of container size, meaning it can handle 20 ft, 40 ft, or other container lengths seamlessly.
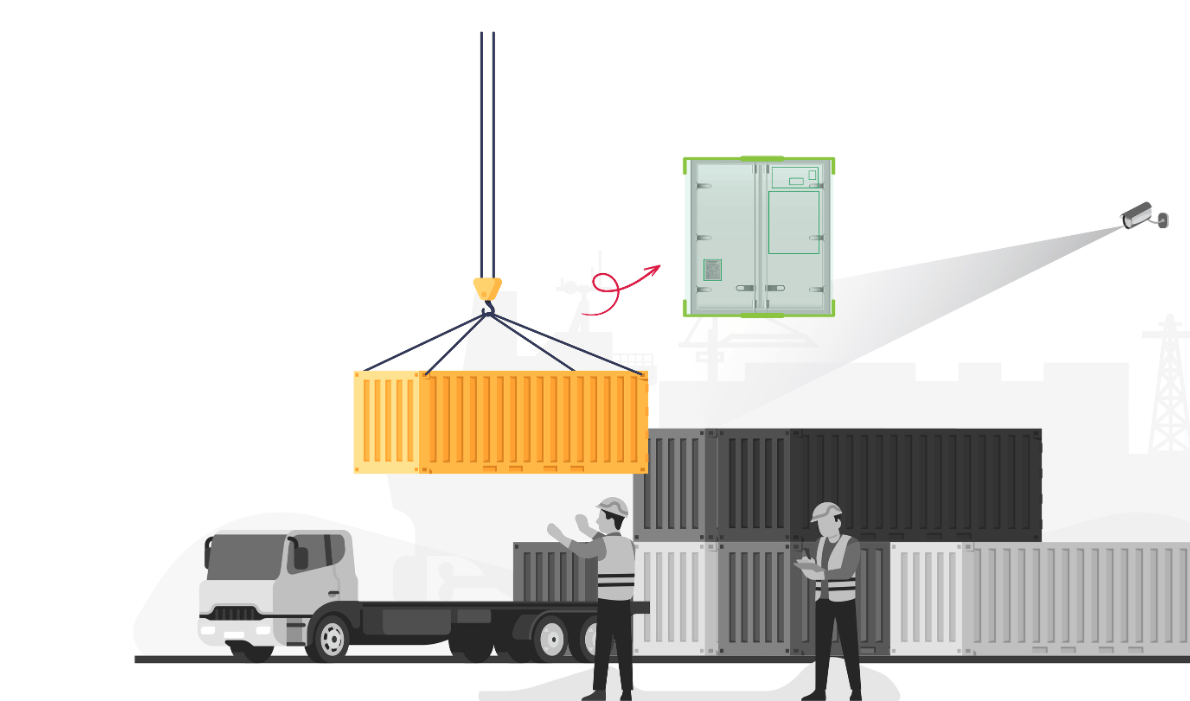
One of the more advanced and transformative modules now being deployed is the AI-driven Container Damage Detection System. This addresses a longstanding challenge: inspecting containers for physical damage (dents, holes, cracks) at the point of entry/exit.
Traditionally, damage inspection was done by human surveyors conducting a visual check, often requiring trucks to stop and potentially causing extra delays if done at the gate. An automated damage detection system uses a set of high-resolution cameras positioned to cover all sides of the container, often as part of the gate OCR portal. As the truck passes through (typically at slow speed, but without stopping), these cameras capture detailed images. Then, AI image analysis algorithms (often leveraging deep learning models) automatically scan the imagery for signs of damage, for example, dents in the container walls, bulges, holes, significant rust patches, or door and structural issues. By comparing to a baseline of what an undamaged container looks like, the AI can pinpoint anomalies and even categorize their severity.
In summary, AI-powered damage detection is like having an expert surveyor at the gate 24/7, but faster and more objective. It keeps operations flowing by removing a manual checkpoint, provides richer data (imagery evidence and analytics on common damage types), and improves safety and customer satisfaction.
Combined with plate and container OCR, this creates a comprehensive picture of each truck/container unit entering or leaving the port, who it is, what its carrying, and in what condition.
While the above three modules focus on the gate transaction itself, a complete automation ecosystem extends into the yard. Container geolocation solutions ensure that once a container is inside the port, its movements and dwell time are continuously tracked. This is typically achieved via AI vision RFID tags or GPS-based IoT devices attached to containers.
Every time the container moves, the system can update its location. Geofences, virtual boundaries defined in the software, can trigger alerts if a container is somewhere it shouldnt be. For example, if a container strays outside the permitted zone or is mistakenly taken to the wrong terminal area, an alarm is raised to notify operators.

Another complementary module is the tracking of container handling equipment activity, exemplified by systems installed on equipment like reach stackers, rubber-tyred gantry cranes , yard trucks or quayside cranes. In our scenario, lets consider the example of Kalmar (a leading equipment manufacturer) and their telematics solutions. By equipping each machine with IoT sensors or a connected telemetry device, ports can monitor key parameters of equipment usage in real time.
For instance, vision cameras and onboard software can log every start/stop cycle of the equipments engine, measure idle time vs active time, count the number of container lifts or moves performed, and track the GPS path the machine travels during operations. Installing such a device on, say, two Kalmar yard cranes or reach stackers yields a wealth of data. This data flows into an analytics dashboard for performance evaluation, often accessible remotely on any computer or tablet.
In summary, container geolocation tracking and equipment activity monitoring extend automation beyond the gate into yard management. They ensure that the benefits of quick gate processing arent lost downstream, the containers journey through the port stays visible and optimized, and the machinery handling containers operates at peak efficiency.
Together, these modules (gate OCR systems, damage detection, tracking, etc.) create a smart gate ecosystem delivering end-to-end automation from entry to exit.
Individually, each module brings a piece of the automation puzzle. But the real power of a modern smart gate system lies in how these components integrate to create a seamless, intelligent workflow.
Before a truck even reaches the gate, the system may already have its appointment in the database. As the truck drives up, an ANPR camera captures its license plate. Immediately, the system cross-references this with expected visits. If the truck is pre-registered, the gate system retrieves the associated container pickup/drop-off order. If not, the truck can be processed as an ad-hoc visit if allowed, or stopped if unauthorized.
As the truck enters, it passes through an OCR portal. Multiple high-speed cameras take images of the truck and container from different angles. The container number OCR module reads the container ID on the back or side of the container. Simultaneously, the ANPR might also catch the trailers license plate if separate. Within a few seconds, the system has identified: Truck ABC 1234 carrying Container XYZU1234567. It verifies the container numbers check digit for accuracy.
While the truck keeps rolling, the images taken are analyzed for container condition. The damage detection AI flags a sizable dent on the containers top right corner, for example. This result is instantly displayed to gate control staff via the dashboard. Depending on port policy, the system could automatically trigger an alert: perhaps a notification is sent to the operations control center that Container XYZU1234567 shows structural dent on entry, severity level 2. The port might still let it in but plan to have it inspected or placed aside for repair if needed.
The boom barrier (if used) lifts and the truck proceeds inside. By now, the integrated system has compiled a digital record: truck and driver ID, container ID, entry time, and condition notes. This data is automatically forwarded to other systems. The system can assign a yard slot; the security system logs the entry; if Customs integration exists, they are informed of the containers arrival status.
Now once inside, suppose the truck carrying that container heads to a yard block. Here the container geolocation module kicks in, perhaps the container was fitted with an RFID tag at the gate or the yard cranes have RFID readers. As soon as the container is placed in the stack, the inventory system knows exactly which slot its in. If the container moves with a yard vehicle, the GPS trackers on that equipment continuously update its journey. Meanwhile, the Kalmar equipment tracker on the yard crane logs that it performed the lift and notes the time and cycle count. In effect, the container is accounted for from gate to ground in the yard, and the equipments contribution is recorded.
When the truck exits the port after dropping the import or after loading an export, the process happens in reverse. At the outbound gate, cameras again identify the truck and container on it. The system checks if that container was authorized to leave (matching it against release orders). It logs the exit time and ensures, for security, that no container leaves unaccounted.
When the gate automation modules are implemented together, ports experience tangible improvements across multiple performance metrics.
Some of the key real-world benefits observed include:
Port gate automation has moved from a futuristic concept to an operational reality delivering measurable gains. In the quest for faster, safer, and more transparent port operations, automating the gateway is a pivotal first step. As weve discussed, technologies like OCR number plate recognition, container code scanning per ISO standards, and AI-driven damage detection work together to eliminate bottlenecks and human error at the entry/exit points of terminals. The addition of container geolocation tracking and equipment monitoring further extends these benefits throughout the port, creating a truly integrated smart system.
Looking ahead, the trend is clear. The port of the future will likely feature fully automated gates, paperless transactions, and vehicles that move in and out with minimal friction. Elements of that future are already here: AI at the gates, IoT in containers, and data driving decisions. Ports that lead this change will position themselves as efficient, customer-friendly nodes in the supply chain, whereas those slow to adapt may face bottlenecks and lost business.
In conclusion, gate automation is a cornerstone of the broader smart port evolution. It brings immediate benefits and sets the stage for further digital transformation.
At WebOccult, we specialize in designing and deploying integrated gate automation solutions that combine AI, OCR, RFID, and advanced analytics to help ports operate smarter and safer. Whether you’re starting with a pilot lane or aiming for full-scale transformation, our team brings the technology and strategic insight needed to deliver results.
Connect with WebOccult today to explore how your port can become a future-ready smart terminal, efficient, secure, and built for the demands of global trade.